...
Diode has sort of internal capacitance in the form of pn layer mix in the pn contact place. When voltage is across diode, some p material goes to n side and some n material goes to p side. This creates "small diode" inside of the main diode. That "blurs" diode orientation and makes diode conduct current in the opposite direction. This lasts for small period of time because then voltage across diode is reversed and this brings diode structure back to normal.
...
Also, it turns out that all diods diodes should emit light. Probably the ones that do not emit light in visible spectrum, emit it to their package wall. (?)
New questions:
- Do all semiconductor diodes emit light?
- Why semiconductor diodes are widely used instead of other types of diodes?
How are they (diodes) made?
...
In laser diode electron and hole can exist near each other for long time, up to microseconds. This creates sort of population inversion. When resonant photon passes by, electron jumps into hole and during this emits coherent photon. In opposite, conventional LED does not wait until photon and emits constantly. Why then some diodes become conventional LEDs, and some - laser diodes?
New questions:
- Why some diodes are constant LEDs, and some - laser diodes?
Further questions T2
Do all semiconductor diodes emit light?
Initial hypothesis: Yes. The ones that emit light in non-visible spectra are covered with package and light is emitted into plastic.
Evaluation of initial hypothesis: there may be somehow different physical mechanism of non-LED diodes work, which doesn’t lead to light emission.
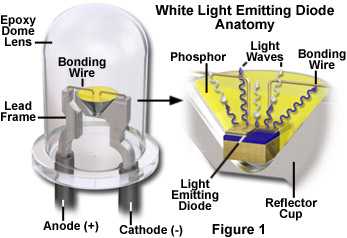
It appears so that all semiconductor diodes emit light. To be exact, all p-n semiconductor junctions emit photons. (Check the picture) Yes yes, but these are not emitted to plastic, they are absorbed back to semiconductor die. This energy is mostly dissipated as heat. LEDs and laser diodes are made so that energy does escape the junction really well.
...
Why semiconductor diodes are widely used instead of other types of diodes?
Initial hypothesis: They are cheapest and the smallest. Which implies that at some point engineers decided that physical principles behind semiconductor diodes allow cheaper and smaller diodes in the next few years. Which means that known non-semiconductor diode’s physical working mechanism contains obstacles that are hard to avoid.
Evaluation of initial hypothesis: On the one side, this is not very good question as it enclosures current state of technological development. On the other side, I tried to make it in the way that it leads to study of physical phenomena and principle, which is good.
Solid-state diodes is used mostly because of its size. Modern mobile phone radio modulator would definitely be of size of the living room, if contained
vacuum tubes. We do not need this huge currents and voltages to calculate and transmit data. However, some radio transmitter towers are using vacuum diodes: this is still very effective solution for very large current applications, where solid state device would just start to melt. There are also differences in current-voltage characteristics .(see picture)
Why some diodes are constant LEDs, and some - laser diodes?
Initial hypothesis: Probably to the use of different materials. Somehow some materials lead to population inversion and some - not. Why? To answer this question, additional study of the materials and outcoming properties are required.
Evaluation of initial hypothesis: Not only materials might be different, but overall geometry and principles may differ as well. However, the word laser diode implies that diode principle stays intact (i.e. it should conduct current in one direction etc.)
To keep it simple, so-called “constant LEDs” are emitting light, when electrons from n-junctions fill the holes in the p-junction. The depletion layer area
between two doped layers is mostly exposed to the plate mirror. Photons are shot here and there, and are focused to one direction with optical cavity.
In the laser diode, optical trap is sandwiched right between p- and n-materials. The junction itself becomes the gain medium. Stimulated emission happens at electron-hole pair: incident photon is forcing the electrons and holes in the junction to annihilate and release photons of light with equal phase and energy.