...
Amplifiers / optical (Minh) -> completed
frequency (PhatThai) -> Thai ?
depending variables (Phat) -> Thai ?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
...
Decibel
Background
The requirement is to understand what is decibel and what it is used for
Initial questions
- What is decibel?
2. How to measure it?
3. How to use it in optical fiber ?
Selected problem
All questions were selected to answer in detail.
My explanation
- Decibel is a universal unit to measure sound level, but it is also used in electronics, signals and communications.
- On the decibel scale, the smallest audible sound (near total silence) is 0 dB. A sound 10 times more powerful is 10 dB. A sound 100 times more powerful than near total silence is 20 dB.
- In my opinion, decibel is used to measure signal loss in transmission in optical fiber.
Critical evaluation
More details and reading as well as reasoning that need to be provided.
Finding more information
Looking for more info about Decibel and also how to use it in fiber optic
Final theory:
The decibel (dB) is used to measure sound level but it is also used widely in communications, electronics and signals. In communications, the decibel is a logarithm way of describing a ratio between two signal power, such as power, sound pressure, voltage, or current levels The decibel is a common measurement used in the field of electronics to determine loss or gain in a system.
Suppose we have 2 signals, signal 1 has a power of P1 watts, signal 2 has a power of P2 Watts, then the difference in decibels between 2 signals is defined to be:
10log(P2/P1)dB where the log is base 10
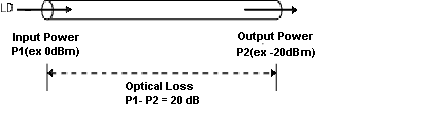
In order to measure optical loss, you can use two units, namely, dBm and dB. While dBm is the actual power level represented in milliwatts, dB (decibel) is the difference between the powers.
Figure 4 – How to Measure Optical Power
Figure 1: How to measure optical power [1]
Light loss, L(dB), is a commonly used specification for fiber optic attenuation. For example, to determine the light loss of an optical fiber in a cable, a light source is connected to one end of the fiber cable (input). The light output power of the source is known to be 0.1 mW. When an optical power meter is connected to the opposite end of the fiber optic cable under test (output), the meter measures 0.05 mW. Using the decibel power loss formula, the optical fiber loss can be calculated as follows:
Figure 2: How to measure fiber loss [2]
The light power loss of this optical fiber is 3 dB
The dB unit is a logarithmic ratio of input and output levels and is therefore not absolute (i.e., has no units). An absolute measure of power in decibels can be made in the dBm form. The dBm unit is a logarithmic ratio of the measured power to 1 mW of reference power
Reference
- Introduction to optical fibers, dB, Attenuation and measurement:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/optical/synchronous-digital-hierarchy-sdh/29000-db-29000.html - Optical Power loss measurement in db- how to measure it fast and correct
http://www.ad-net.com.tw/?id=474
Other Variable Dependencies
Background
The requirement is to understand what factors and dependencies cause attenuation in fiber optic.
Initial questions
How does attenuation happen?
What kind of factors cause the attenuation ?
Selected problem
All questions were selected to answer in detail.
My explanation
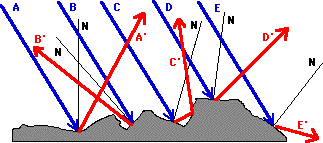
Attenuation affects the quality of the signal transmission. Attenuation can be caused by long transmission line and the signal loses its energy while transmitting.
Critical evaluation
My explanation is not detailed enough and more investigations need to be done to understand more deeply.
Finding more information
More information is obtained by reading books and searching for online information.
Final theory
- Reflection and the Ray Model of Light - Lesson 1 - Reflection and its Importance
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/Lesson-1/Specular-vs-Diffuse-Reflection - B.G. Potter. Module 3 - Attenuation in optical fibers
http://opti500.cian-erc.org/opti500/pdf/sm/Module3%20Optical%20Attenuation.pdf