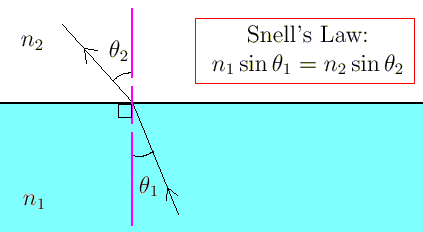Refractive index
Refractive Index is dimensionless number that describes how light, or any other radiation, propagates through that medium. The refractive index determines how much light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. It is defined as
, where c= speed of light in vacuum, v= speed of light in any medium and n= refractive index of that medium
Snell's law
Snell's law, also known as the law of refraction, states that the ratio of sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of velocities of the incidence and the refracted medium,also equal to the reciprocal to the ratio of refractive indices.i.e sinθ1/sinθ2 =V1 / V2 = n2 / n1.
where : θ = angle from the normal
v= velocity of light in the respective medium.
n =Reflective index (n = c/v)
The light travelling from a medium with lower refractive index to a medium with higher refractive index bends towards the normal and vice versa.
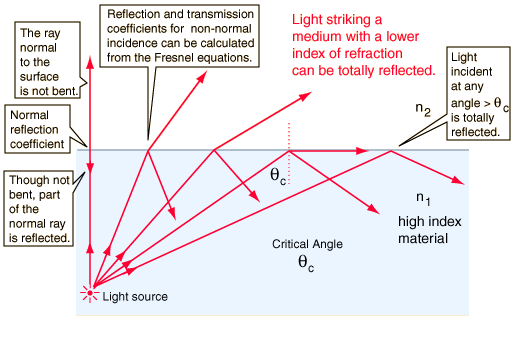
Critical angle
When the incidence ray passes from dense medium to rare at such an angle that the refracted ray is 90 degrees to the normal, it is called the critical angle. This angle depends on the medium it travels to and from.
Total internal reflection
When the incidence ray passes at such an angle which is greater than 90 degrees, the light gets reflected into the same medium instead of getting refracted, this process is known as total internal reflection.